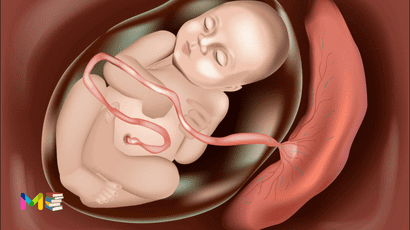
Oligohydramnios is a problem that occur during pregnancy, characterized by the deficiency of amniotic fluid, the fluid that surrounds the fetus in the womb. It can cause pregnancy complications or be a sign of an underlying health condition.
Not all fetuses develop abnormalities because of low levels of amniotic fluid. The occurrence of Oligohydramnios sequence depends on a few factors:
- The stage of pregnancy.
- The level of amniotic fluid.
The later stages of pregnancy appear to be the most troublesome. If amniotic fluid deficiency sequence occurs at that time, the more serious the condition can be.
Amniotic fluid deficiency affects about 4% of pregnant women. It’s most common in the last three months of pregnancy. This rate rises to about 12% in people who are past their due date because amniotic fluid levels decrease after 40 weeks of pregnancy.
Table of Contents
The amniotic fluid
Amniotic fluid is the clear liquid that surrounds your baby in the uterus during pregnancy. It is produced soon after the amniotic sac forms at about 12 days after conception. It is first made up of water that is provided by the mother, and then around 20 weeks of fetal urine, becomes the primary substance.
As the fetus develop, he or she will move and tumble in the womb with the help of the amniotic fluid. During the second trimester, the fetus will begin to breathe and swallow the amniotic fluid. In some cases, the amniotic fluid may measure too low or too high. If the measurement of amniotic fluid is too low it is called oligohydramnios, but If too high it is called polyhydramnios.
Functions of the amniotic fluid
There’re several function of the amniotic fluid, this include:
- It provide support and protects the baby from fetal injury.
- It also allows room for growth, movement and development.
- It helps maintain a constant temperature.
- It helps lubricate the fetus’s body parts and prevents them from fusing
- It has nutrients, hormones, and antibodies that help to fight off infections.
- In relation to the umbilical cord, it prevents it from being squeezed between the baby and the wall of the uterus.
Healthcare professionals measure the amount of amniotic fluid through a few different methods, most commonly through:
- amniotic fluid index (AFI) evaluation
- deep pocket measurements (DPM)
If an AFI shows a fluid level of fewer than 5 centimeters (or less than the 5th percentile), the absence of a fluid pocket 2-3 cm in-depth, or a fluid volume of less than 500mL at 32-36 weeks gestation, then a diagnosis of oligohydramnios would be confirmed.
You can also read about causes and symptoms of preeclampsia
Causes of Oligohydramnios
Several things can contribute or cause amniotic fluid deficiency, these include:
- Congenital anomalies or birth defects. Problems with the development of the kidneys or urinary tract which could cause little urine production, leading to low levels of amniotic fluid.
- Problems with the placenta. If the placenta is not providing enough blood and nutrients to the baby, then the baby may stop recycling fluid.
- Prelabor rupture of the membranes. This may be a gush of fluid or a slow constant trickle of fluid. This is due to a tear in the membrane. Premature rupture of membranes (PROM) can also result in low amniotic fluid levels.
- Going more than two weeks past your due date (Post Date Pregnancy). A postdate pregnancy (one that goes over 42 weeks) can have low levels of amniotic fluid, which could be a result of declining placental function.
- Maternal Complications or problems. Factors such as maternal dehydration, hypertension, preeclampsia, diabetes, and chronic hypoxia can have an effect on amniotic fluid levels.
- Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome.
Symptoms of oligohydramnios
Several signs and symptoms occur when amniotic fluid is too low. Limited amniotic fluid makes the ammonic cavity smaller than normal. This constricts the fetus, which interferes with normal development and growth.
Signs and symptoms in the fetus may include:
- low set ears
- widely spaced eyes
- broad nasal bridge
Signs and symptoms in the pregnant woman may include:
- You’re leaking fluid from your vagina.
- Your uterus measures small.
- You don’t feel your baby move enough.
- You’re not gaining enough weight.
When the sequence of amniotic fluid deficiency is caused by fetal kidney failure, urine output after birth is low or absent. Limited amniotic fluid also interferes with normal lung development. If a baby survives through birth, he or she may later have difficulty in breathing.
Risk factors of oligohydramnios
Amniotic fluid deficiency sequence most commonly affects male babies. There appears to be a genetic reason for some causes of fetus kidney failure.
Also a family history of certain renal diseases may increase a pregnant woman risk of developing amniotic fluid deficiency sequence during pregnancy.
Complications of oligohydramnios
Low amniotic fluid in the first six months of pregnancy is generally more dangerous. The following are the complications that can occur during this period:
- Infection if your water has broken early.
- Deformities caused by being compressed in your uterus.
- Miscarriage.
- Preterm birth.
- Stillbirth.
If diagnosed with amniotic fluid deficiency in the last trimester, that is 28 to 40 weeks of pregnancy, complications can include:
- Umbilical cord compression.
- Increased risk for infection if your water has broken too early.
- Fetal growth restriction.
- Respiratory issues or underdeveloped lungs.
- Need for an early delivery.
- Increase risk of Cesarean delivery.
You can also read about risk factors and complications of abnormal uterine bleeding
Prevention of oligohydramnios
Unfortunately, there is currently no known prevention for oligohydramnios sequence. The best thing to do is to be attending all prenatal checkups and be honest with your healthcare provider about your symptoms and medical history. Knowing if you’re at risk for low amniotic fluid is your best chance for treating the condition on time.
Diagnosis of oligohydramnios
Healthcare provider will diagnose oligohyramnios sequence with an ultrasound. An ultrasound can detect low levels of amniotic fluid and abnormal kidney development in the fetus.
Two ways to measure the amniotic fluid include:
- amniotic fluid index (AFI)
- maximum vertical pocket or deep pocket measurements (DPM)
After the delivery of a baby, an X-ray of the lungs and kidneys can help your provider check for abnormal fetal development. This can also help diagnose amniotic fluid deficiency sequence in a newborn.
Treatment of oligohyramnios
The management for low amniotic fluid levels depend on the gestational age. As a pregnant woman, If you are not a full term yet, your healthcare provider will monitor you and your levels very closely.
Tests such as non-stress and contraction stress test may be done to monitor the fetus’s activity. If you are close to full term, then delivery is usually what most healthcare professionals recommend in situations of low amniotic fluid levels.
Other treatment options include:
- Maternal re-hydration with oral fluids or IV fluids has shown to help increase amniotic fluid levels.
- Injection of fluid prior to delivery through amniocentesis. The condition of oligohydramnios is reported to often return within one week of this procedure, but it can aid in helping doctors visualize fetal anatomy and make a diagnosis.
- If you have low amniotic fluid during labor, your healthcare provider might consider a procedure in which saline is put into your uterus via a catheter placed through the cervix. This procedure is called amnioinfusion. This is typically done during labor if your healthcare provider notice problems with the baby’s heart rate.
A baby can be born healthy and happy. Having low amniotic fluid can be serious, but in most of the cases, it’s highly treatable. If you have any other concerns about oligohydramnios, you should consult your doctor for more knowledge.
- List of Common Diseases & Medical Disorders
- Buy Complete Premium Anatomy Notes (PDFs)
- Medmichihealthcare New posts
- Read All causes of disease short notes
- Read All diagnosis of disease short notes
- Read All treatment of disease short notes
- Subscribe Medmichihealthcare YouTube channel
Discover more from Medmichihealthcare
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.