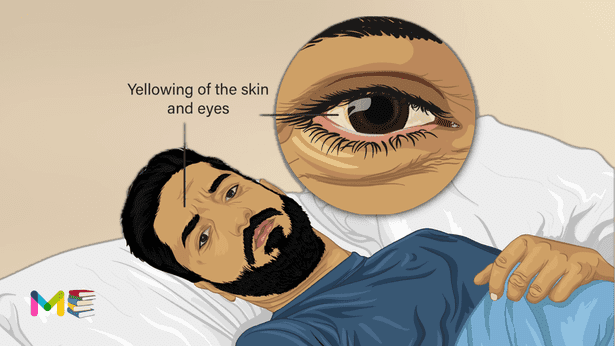
Jaundice in adults is the yellow discolouration of your skin, the whites of your eyes (sclera) and mucous membranes. This yellow color is caused by a high level of bilirubin in the body, a yellow-orange bile pigment. Jaundice in adults has many causes, including hepatitis, gallstones and tumors.
Bilirubin is formed from the breakdown of red blood cells. When the liver is not working properly, it can cause bilirubin to build up in the blood. If too much bilirubin is left in your system, you can develop hyperbilirubinemia. This can lead to jaundice, which causes your skin and the whites of your eyes to turn yellow.
Jaundice can develop in people of all ages and is normally the result of an underlying condition. Newborns and older adults have the highest likelihood of developing jaundice.
Table of Contents
Types of jaundice
There are four main types of jaundice, which are grouped by where the bilirubin collects in your body. These include:
- Prehepatic jaundice. If bilirubin builds up before blood enters the liver, it’s known as prehepatic jaundice. This means you’re breaking down red blood cells and creating more bilirubin than your liver can process.
- Hepatic jaundice. If your liver isn’t able to process bilirubin well, it’s called hepatic jaundice.
- Posthepatic jaundice. Posthepatic jaundice is when bilirubin builds up after passing through the liver and your body can’t clear it quickly enough.
- Obstructive jaundice. This is when bile isn’t able to drain into your intestines because of a blocked or narrow bile or pancreatic duct. This type of jaundice has a high death rate, so it’s important to catch and treat it early.
You can also read about types and symptoms of appendicitis
Symptoms of jaundice in adults
The severity of symptoms of jaundice in adults depends on the underlying causes and how quickly or slowly the disease develops. If you have a short-term case of jaundice (usually caused by infection), you may have the following symptoms and signs:
- Fever.
- Chills.
- Abdominal pain.
- Flu-like symptoms.
- Change in skin color.
- Dark-colored urine and/or clay-colored stool.
- Confusion
- Abnormal drowsiness
If jaundice isn’t caused by an infection, you may have symptoms such as weight loss or itchy skin (pruritus). If the jaundice is caused by pancreatic or biliary tract cancers, the most common symptom is abdominal pain. Sometimes, you may have jaundice occurring with liver disease if you have:
- Chronic hepatitis or inflammation of the liver.
- Pyoderma gangrenosum (a type of skin disease).
- Acute hepatitis A, B or C.
- Polyarthralgias (inflammation of the joints).
Causes of jaundice in adults
Jaundice in adults is rare, but you can get it for many reasons. These include:
- Reabsorption of a large hematoma (a collection of clotted or partially clotted blood under the skin).
- Hemolytic anemias (blood cells are destroyed and removed from the bloodstream before their normal lifespan is over).
- Viruses, including Hepatitis A, chronic Hepatitis B and C, and Epstein-Barr virus infection (infectious mononucleosis).
- Alcohol.
- Autoimmune disorders.
- Rare genetic metabolic defects.
- Medicines, including acetaminophen toxicity, penicillins, oral contraceptives, chlorpromazine and estrogenic or anabolic steroids.
- Gallstones.
- Inflammation (swelling) of the gallbladder.
- Gallbladder cancer.
- Pancreatic tumor.
How long jaundice lasts depends on what’s causing it and the treatment you need. If a medication is causing it, jaundice will fade after you stop taking it. If hepatitis is causing it, medications can be taken to treat the condition. If there is a blocked bile duct or gallstones, surgery may be required.
You can also read about symptoms and causes of liver cirrhosis
Risk factors of jaundice in adults
The following are some of the risk factors of jaundice in adults:
- Drink too much alcohol
- Have hepatitis
- People during middle age
- Having one or several liver problems
Prevention of jaundice in adults
There is no clear way to prevent jaundice in adults, as it can be caused by different conditions. But you can reduce your risk of jaundice through lifestyle changes. These include:
- Avoid herbal supplements (which can be toxic to the liver) unless recommended by your doctor
- Stop smoking
- Reduce or cut out all alcohol (the CDC recommends no more than two alcoholic drinks per day for men and one daily for women)
- Don’t use intravenous drugs (drugs that go into your vein)
- Don’t take more prescription medication than you are prescribed
- Get all recommended vaccines before traveling overseas
- Use safe sex practices
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Keep your cholesterol in a healthy range
You can also read about risk factors and prevention of high cholesterol
Diagnosis of jaundice in adults
Your healthcare provider will ask about your medical history and perform physical exam. During an examination, your doctor will pay attention to your abdomen, liver, and skin.
Doctors diagnose jaundice by checking for signs of liver disease such as:
- Bruising of the skin.
- Spider angiomas (abnormal collection of blood vessels near the surface of the skin).
- Palmar erythema (red coloration of the palms and fingertips).
Your doctor may include lab tests to help determine the underlying cause of jaundice. These include:
- Bilirubin tests: A high level of unconjugated bilirubin compared to levels of conjugated bilirubin suggest hemolytic jaundice.
- Urinalysis (urine testing). Urinalysis that’s positive for bilirubin shows that the patient has conjugated jaundice. The findings of urinalysis should be confirmed by serum testing.
- Full blood count (FBC) or complete blood count (CBC): This measures levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
- Hepatitis A, B, and C tests: This tests for a range of liver infections.
Your doctor will also do an exam to determine the size and tenderness or obstruction of your liver. These include:
- Imagine tests. including MRI, CT, and ultrasound scans. In addition, they may carry out an endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). This is a procedure combining endoscopy and X-ray imaging.
- Liver biopsy. A liver biopsy can check for inflammation, cirrhosis, cancer, and fatty liver. This test involves inserting a needle into the liver to obtain a tissue sample. A healthcare professional will then examine the sample under the microscope.
You can also read about diagnosis and treatment of Japanese encephalitis
Treatment of jaundice in adults
Treatment depends on the underlying cause of jaundice.
If you have acute viral hepatitis, jaundice will go away on its own as your liver heals. If a blocked bile duct is to blame, your doctor may suggest surgery to open it. If your skin is itching, your doctor can prescribe cholestyramine to be taken by mouth. This medication is used to remove bile acids from your body, which cause itching.
To relieve symptoms of jaundice caused by hepatitis, you should:
- get plenty of rest
- drink lots of fluids
- avoid alcohol
- avoid medicines that impact the liver
Your doctor might suggest surgery for other causes of jaundice such as:
- gallstones
- a blocked bile duct
- pancreatic cancer
Surgery may involve placement of a stent. This lets the bile (digestive fluid made by your liver) flow past the blockage.
Phototherapy. This uses a fluorescent white or blue-spectrum light that breaks down bilirubin so it can be released from the body. This treatment is used for newborns, but phototherapy has not been shown to be effective for treating jaundice in adults.
- List of Common Diseases & Medical Disorders
- Buy Complete Premium Anatomy Notes (PDFs)
- Medmichihealthcare New posts
- Read All causes of disease short notes
- Read All diagnosis of disease short notes
- Read All treatment of disease short notes
- Subscribe Medmichihealthcare YouTube channel
Discover more from Medmichihealthcare
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.